“Electing these dictatorships as UN judges on human rights is like making a gang of arsonists into the fire brigade,” said Hillel Neuer, executive director of UN Watch.
By Associated Press
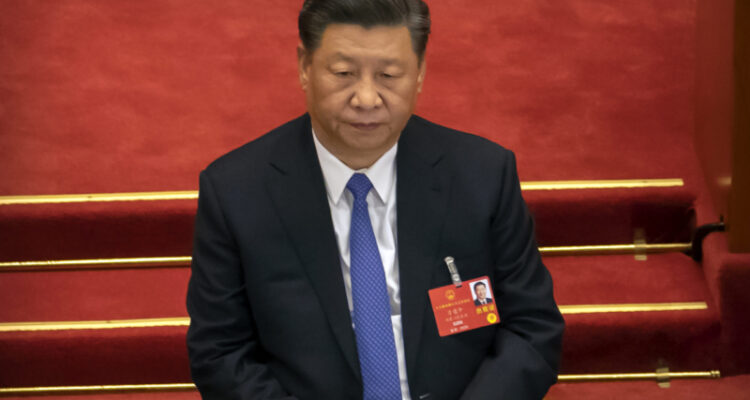
China and Cuba won seats on the UN’s premiere human rights body Tuesday despite opposition from activist groups over their abysmal human rights records, but another target, Saudi Arabia, lost.
Russia, which also won a seat on the council, and Cuba were running unopposed, but China and Saudi Arabia were in a five-way race in the only contested race for seats on the Human Rights Council.
In that race, Pakistan received 169 votes, Uzbekistan 164, Nepal 150, China 139 and Saudi Arabia just 90 votes.
The United States announced its withdrawal from the council in June 2018 because of the body’s virulently anti-Israel agenda and its record as an unrepentant forum for hypocrisy about human rights.
Under the Human Rights Council’s rules, seats are allocated to regions to ensure geographical representation.
Except for the Asia-Pacific contest, the election of 15 members to the 47-member Human Rights Council was all but decided in advance because all the other regional groups had uncontested slates.
Four countries won four Africa seats: Ivory Coast, Malawi, Gabon and Senegal. Russia and Ukraine won the two East European seats. In the Latin American and Caribbean group, Mexico, Cuba and Bolivia won the three open seats. And Britain and France won the two seats for the Western European and others group.
Last week, a coalition of human rights groups from Europe, the United States and Canada called on UN member states to oppose the election of China, Russia, Saudi Arabia, Cuba, Pakistan and Uzbekistan, saying their human rights records make them “unqualified.”
“Electing these dictatorships as U.N. judges on human rights is like making a gang of arsonists into the fire brigade,” said Hillel Neuer, executive director of UN Watch.
The Geneva-based rights organization published a 30-page joint report with the Human Rights Foundation and the Raoul Wallenberg Center for Human Rights evaluating candidates for council seats. The report lists Bolivia, Ivory Coast, Nepal, Malawi, Mexico, Senegal and Ukraine as having “questionable” credentials due to problematic human rights and U.N. voting records that need improvement. It gave “qualified” ratings only to the United Kingdom and France.
Human Rights Watch pointed to an unprecedented call by 50 UN experts on June 26 for “decisive measures to protect fundamental freedoms in China,” warning about its mass rights violations in Hong Kong and Tibet and against ethnic Uighurs in the Chinese province of Xinjiang as well as attacks on rights defenders, journalists, lawyers and government critics. Their call was echoed by over 400 civil society groups from more than 60 countries.
The rights group said Russia’s military operations with the Syrian government “have deliberately or indiscriminately killed civilians and destroyed hospitals and other protected civilian infrastructure in violation of international humanitarian law,” and noted Russia’s veto of UN Security Council resolutions on Syria, including blocking Damascus’ referral to the International Criminal Court.
The Geneva-based Human Rights Council can spotlight abuses and has special monitors watching certain countries and issues. It also periodically reviews human rights in every UN member country.
Created in 2006 to replace a commission discredited because of some members’ poor rights records, the new council soon came to face similar criticism.